Wallets & Signer¶
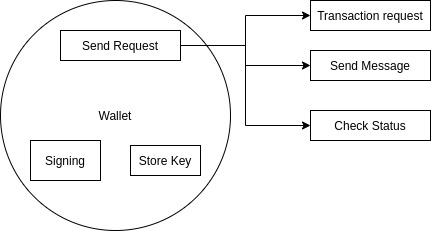
- Wallet’s main functions are to:
- Manage key, which will be used for encryption and decryption
- Sign, encrypt transaction or message before it is sent through network provider
- Send request to blockchain via network provider
Wallet¶
The wallet implements the Signer API that can be used where a Signer is expected and has all the required properties.
Create Wallet¶
- Wallet . createRandom ( [ options ] ) => Wallet
- Creates a new random wallet, then generate mnemonic phrases and an encrypted JSON file.Ensure this infomation is stored somewhere safe, there is NO way to recover it if lost.Parameters can be use are:
- entropyLength: int (from 16 to 32 & mutiplications of 4—higher value means greater security)
- path: string (directory to store mnemonic)
- locale: string (wordlists)
The current supported wordlists are:
Language node.js English (US) wordlists.enSpanish wordlists.esFrance wordlists.frItalian wordlists.itJapanese wordlists.jaKorean wordlists.koChinese (simplified) wordlists.zh_cnChinese (traditional) wordlists.zh_tw
Warning
It is highly recommended to show mnemonic of the wallet to the users and advise them to write it down because there is no way to recover their wallet without the mnemonic phrases. Writing down private key or JSON file on a paper is not practical.
//By default, the wallet is created by 16 hexadecimal digits private key,
//and will generate mnemonic using wordlists.en
let randomWallet = mxw.Wallet.createRandom();
console.log("Address:", randomWallet.address);
//expected result:
//a random string, it will look something like this
//mxw1duct5rv3wan3vpdk3ms6kgn0j8h905kqvccw4r
// Create a wallet using 24 hexadecimal digits
let randomWallet = mxw.Wallet.createRandom({
entropyLength: 24
});
console.log("Address:", randomWallet.hexAddress);
//expected result:
//a random hexstring, it will looks something like this
//0xd450137C0b463260F7Ef77177288De3976078129
// Create a wallet and generate mnemonic using wordlists.zh
let randomWallet = mxw.Wallet.createRandom({
locale: mxw.wordlists.zh
});
console.log("Mnemonic:", randomWallet.mnemonic);
//expected result:
//Mnemonic: "followed by 12 random Chinese words"
Note
There is no way to differentiate or know how many digits are used to create the wallet.
Create Instance of Existing Wallet¶
There are 3 ways to load a wallet: private key, mnemonic, and JSON file. If a user doesn’t have any one of these, it is impossible to recover the wallet.
- new Wallet ( privateKey [ , provider ] )
- Creating a new instance of existing wallet from private key and connect a provider (optional).
//connect wallet to localnet
let privateKey = "0x0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef";
let networkProvider = mxw.getDefaultProvider("localnet");
let walletWithProvider = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey, provider);
- prototype . connect ( provider ) => Wallet
- Creates a new wallet instance from an existing instance, connect to a new provider.
//load wallet using private key
let privateKey = "0x0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef";
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey);
// Connect the wallet to localnet
let networkProvider = mxw.getDefaultProvider("localnet");
wallet.connect(provider);
- Wallet . fromEncryptedJson ( json, password [ , progressCallback ] ) => Wallet
- Creating a new instance of existing wallet by decrypting an encrypted Secret Storage JSON Wallet (from created from prototype.encrypt).
let data = {
address: "mxw1x7tp9tt7mu0jm6qdmljgntvzzp53lrtndr7h8x",
id: "0a462eb4-939d-4d05-acb1-f7827f758e3c",
version: 3,
Crypto: {
cipher: "aes-128-ctr",
cipherparams: {
iv: "ff1e5fd9e71497a11e2923e7a2496bb9"
},
ciphertext: "6caeb28cf0687c9c84d5f02dab1afe3f27fb85483f90538ca59d299c5f2d426f",
kdf: "scrypt",
kdfparams: {
salt: "8e8462bc7808066ba66d85fb85111906665b04b2320b5e7ac615d81e4f0641b5",
n: 131072,
dklen: 32,
p: 1,
r: 8
},
mac: "b7927c99583d62ec2426220fc5b65872aa89183227def48fd7b150b566c12142"
},
x-mxw: {
client: "mxw-sdk",
filename: "UTC--2019-07-25T16-24-39.0Z--mxw1x7tp9tt7mu0jm6qdmljgntvzzp53lrtndr7h8x",
mnemonicCounter: "0de98c10a68756d8d7c51f4460f9d2cb",
mnemonicCiphertext: "a31bb80eecb99a44eddbb53897e74f38",
path: "m/44'/376'/0'/0/0",
version: "0.1"
}
};
let json = JSON.stringify(data);
let password = "any strong password";
mxw.Wallet.fromEncryptedJson(json, password).then((wallet) => {
console.log("Wallet: " + wallet.address);
// expected result:
// mxw1x7tp9tt7mu0jm6qdmljgntvzzp53lrtndr7h8x
});
- Wallet . fromMnemonic ( mnemonic [ , path = “m/44’/376’/0’/0/0” [ , wordlist ] ] ) => Wallet
- Generates a BIP-039 + BIP-044 wallet from mnemonic deriving path using the wordlist. The default language is English (en).
let mnemonic = "legal grain canyon open antenna flame destroy nature fall pistol mushroom stay";
let mnemonicWallet = mxw.Wallet.fromMnemonic(mnemonic);
console.log("mnemonicWallet: " + mnemonicWallet.address);
// expected result:
// mnemonicWallet: mxw1x7tp9tt7mu0jm6qdmljgntvzzp53lrtndr7h8x
// Load the second account from a mnemonic
let path = "m/44'/376'/1'/0/0";
let secondMnemonicWallet = mxw.Wallet.fromMnemonic(mnemonic, path);
console.log("secondMnemonicWallet: " + secondMnemonicWallet.address);
// expected result:
// secondMnemonicWallet: mxw1lgz72w89amz76vrnl3mgfj4p9jls7eggts0pag
// Load using a non-english locale wordlist (the path "null" will use the default)
let zhMnemonic = "手 农 勾 讲 嫂 蒋 借 棚 遗 没 紫 雾";
let zhMnemonicWallet = mxw.Wallet.fromMnemonic(zhMnemonic, null, mxw.wordlists.zh);
console.log("zhMnemonicWallet: " + zhMnemonicWallet.address);
// expected result:
// zhMnemonicWallet: mxw1j4yh2gfumy8d327n0uvztg9075fjzd59vxf9ae
Prototype Variables¶
These are the variables you can get from wallet.
- prototype . address
- Returns public address of a wallet.data type: string
- prototype . privateKey
- Returns private key of a wallet; always keep this secret.data type: hex string
- prototype . provider
Returns a connected Provider which allows the wallet to connect to the blockchain network to query its state and send transactions, or null if no provider is connected.
To change the provider, use the connect method, which will return a new instance of the wallet connected to the provider.
data type: string- prototype . mnemonic
- Returns mnemonic phrase for this wallet, or null if the mnemonic is unknown.data type: string
- prototype . path
- Returns mnemonic path for this wallet, or null if the mnemonic is unknown.data type: string
Signers¶
Signer is required to add a layer of security in a transaction, ensuring no one can manipulate other’s wallet
Signing¶
An encryption process using user’s own private key. When sending message or transaction to another wallet, it will be encryted again using their public key.
- prototype . signMessage ( message ) => Promise<string>
Signs message and returns a Promise that resolves to the flat-format signature.
If message is a string, it is converted to UTF-8 bytes, otherwise it is preserved as a binary representation of the Arrayish data.
let privateKey = "0xca250aeca008d36b4b4ff83709343c9e4c4ea461e5aa5fa51d57a0fe11eb045e";
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey);
// Sign a text message
return wallet.signMessage("Hello Blockchain!").then((signature) => {
// Flat-format
console.log(signature);
// expected result:
// 0xc49045d2fd3f591c86b1c35ed90315f6b42791401854c5164461946c8f5fea98
// 0229683de3459716cd7d1e5f9502811766a5eaf9c96c64c1625aaad815cdc3741c
// Expanded-format
console.log(mxw.utils.splitSignature(signature));
// expected result:
// {
// r: "0xc49045d2fd3f591c86b1c35ed90315f6b42791401854c5164461946c8f5fea98",
// s: "0x0229683de3459716cd7d1e5f9502811766a5eaf9c96c64c1625aaad815cdc374",
// v: 28,
// recoveryParam: 1
// }
});
let privateKey = "0xca250aeca008d36b4b4ff83709343c9e4c4ea461e5aa5fa51d57a0fe11eb045e";
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey);
// The 66-character hex string MUST be converted to a 32-byte array first!
let hash = "0x48656c6c6f20426c6f636b636861696e21";
let binaryData = mxw.utils.arrayify(hash);
wallet.signMessage(binaryData).then((signature) => {
console.log(signature);
// expected result:
// "0xc49045d2fd3f591c86b1c35ed90315f6b42791401854c5164461946c8f5fea98
// 0229683de3459716cd7d1e5f9502811766a5eaf9c96c64c1625aaad815cdc3741c
let address = mxw.utils.verifyMessage(binaryData, signature);
console.log(address);
// expected result:
// Should be equal to the signer's wallet address: mxw1x7tp9tt7mu0jm6qdmljgntvzzp53lrtndr7h8x
});
- prototype . sign ( transaction ) => Promise<string>
Signs transaction and returns a Promise that resolves to the signed transaction as a hex string.
In general, the sendTransaction method is preferred to
sign, as it can automatically populate values asynchronously.Check out Transactions and Transaction Reciepts for more details.
let privateKey = "0xca250aeca008d36b4b4ff83709343c9e4c4ea461e5aa5fa51d57a0fe11eb045e";
let networkProvider = mxw.getDefaultProvider("localnet");
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey, networkProvider);
console.log(wallet.address);
// expected result:
// "mxw1x7tp9tt7mu0jm6qdmljgntvzzp53lrtndr7h8x"
let amount = mxw.utils.parseMxw("1.0");
// All properties are optional, except fee
let transaction = {
type: "cosmos-sdk/StdTx",
value: {
msg: [
{
type: "mxw/MsgSend",
value: {
amount: [
{
amount: amount,
denom: "cin",
},
],
from_address: wallet.address,
to_address: "mxw1j4yh2gfumy8d327n0uvztg9075fjzd59vxf9ae",
}
}
],
memo: "Hello Blockchain"
},
fee: provider.getTransactionFee("bank", "bank-send")
};
wallet.sign(transaction).then((signedTransaction) => {
console.log(signedTransaction);
// Should be Base64 encoded string
provider.sendTransaction(signedTransaction).then((tx) => {
console.log(tx);
// Should be transaction response with transaction hash value
// Query transaction receipt by transaction hash
provider.waitForTransaction(tx.hash).then((receipt) => {
console.log(receipt.status);
//expected result:
//1 (means success)
});
});
});
Cryptographic Functions¶
Shared secret is used when two parties agree on sharing their asset inside a blockchain. After a shared secret is computed, it will return as a hex string. The hex string can be used for authentication purpose of any operations involved in their asset sharing.
- prototype . computeSharedSecret ( otherPublicKey ) => hex string
- Computes the shared secret by using receiving wallet’s public key and return it as a hex string. In general, the shared secret should not be used directly as encryption key. Instead, it can be derived it using Password-Based Key Derivation Function 2 (PBKDF2).
let wallet = mxw.Wallet.createRandom();
let otherWallet = mxw.Wallet.createRandom();
console.log(wallet.computeSharedSecret(otherWallet.publicKey));
//expected result:
//a hex string, something like this
//0xcdfa6c550d930fa45b9f938a96a3b76c90e1f90fed7ffd8bbcc6dbd566316e88
Blockchain Operations¶
These operations require wallet to be connected to blockchain by a network provider.
- prototype . getBalance ( ) => Promise<BigNumber>
- Returns a Promise that resolves to the balance of the wallet (as a BigNumber, in cin). Be aware that the number of decimals for cin is 18. The balance can be converted to a human-readable format by formatMXW, versa parseMXW.
let networkProvider = mxw.getDefaultProvider("localnet");
let privateKey = "0x0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000001";
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey,networkProvider);
wallet.getBalance().then((balance)=>{
console.log(mxw.utils.formatMxw("Wallet balance: " + balance));
});
// Expected result
// Wallet balance: 0.0
- prototype . getTransactionCount ( ) => Promise<BigNumber>
- Returns a Promise that resolves to the number of transactions this account has ever sent (as a BigNumber).
// We require a provider to query the network
let networkProvider = mxw.getDefaultProvider("localnet");
let privateKey = "0x0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef";
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey, networkProvider);
wallet.getBalance().then((balance) => {
console.log("Balance: " + mxw.utils.formatMxw(balance));
//expected result:
//Balance: 0.0
});
wallet.getTransactionCount().then((nonce) => {
console.log("Transaction Count: " + mxw.utils.formatMxw(nonce));
//expected result:
//Transaction Count: 0.0
});
- prototype . transfer ( AddressOrName, value ) => Promise<TransactionReceipt>
Sends the transfer transaction to the network and returns a Promise that resolves to a Transaction Receipt.
The AddressOrName can be set to recipient’s alias or wallet address. The
valueis the number of cin (as a BigNumber) that is being transferred to recipient. Be aware that the number of decimals for cin is 18.
// We require a provider to send transactions
let networkProvider = mxw.getDefaultProvider("localnet");
let privateKey = "0x0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef0123456789abcdef";
let wallet = new mxw.Wallet(privateKey, networkProvider);
let to = "mxw1j4yh2gfumy8d327n0uvztg9075fjzd59vxf9ae";
// ... or supports alias names
// to: "jeansoon",
let amount = mxw.utils.parseMxw("1.0");
// We must pass in the amount as cin (1 MXW = 1e18 cin), so we
// use this convenient function to convert MXW to cin.
wallet.transfer(to, amount).then((receipt) => {
console.log(receipt.status);
//expected result:
//1 (means success)
});
- prototype . sendTransaction ( transaction ) => Promise<TransactionResponse>
- Sends the transaction (see Transaction Requests) to the network and returns a Promise that resolves to a Transaction Response. Any properties that are not provided will be populated from the network.
Encrypted JSON Wallets¶
Many systems store private keys as encrypted JSON wallets, in various formats. There are several formats and algorithms that are used, all of which are supported to be read. Only the secure scrypt variation can be generated.
See Wallet.fromEncryptedJson for creating a wallet instance from a JSON wallet.
- prototype . encrypt ( password [ , options [ , progressCallback ] ] ) => Promise<string>
Encrypts the wallet as an encrypted JSON wallet, with the password.
All options are optional. The valid options are:
- salt — the salt to use for scrypt
- iv — the initialization vector to use for AES-256-CTR
- uuid — the UUID to use for the wallet
- scrypt — the scrypt parameters to use (N, r, and p)
- entropy — the mnemonic entropy of this wallet; generally you should not specify this
- mnemonic — the mnemonic phrase of this wallet; generally you should not specify this
- path — the mnemonic path of this wallet; generally you should not specify this
If the progressCallback is specified, it will be called periodically during encryption with a value between 0 and 1, inclusive of indicating the progress.
let password = "any strong password";
function callback(progress) {
console.log("Encrypting: " + parseInt(progress * 100) + "% complete");
}
return wallet.encrypt(password, callback).then((json) => {
console.log(json);
// expected result:
// an encrypted wallet JSON.
return mxw.Wallet.fromEncryptedJson(json, password).then((decryptedWallet)=>{
console.log(decryptedWallet);
// expected result:
// a decrypted wallet object.
});
});
Signer API¶
The Signer API is an abstract class which makes it easy to extend and add new signers, that can be used by this library and extension libraries. The wallet extends the Signer API.
To implement a signer, inherit the abstract class mxw.types.Signer and implement the following properties:
- object . provider
- Returns Provider that is connected to the network. This is optional, however, without a provider, only write-only operations should be expected to work.
- object . getAddress ( ) => Promise<Address>
- Returns a Promise that resolves to the account address.
- object . signMessage ( message ) => Promise<hex>
Returns a Promise that resolves to the Flat-Format Signature for the message.
If message is a string, it is converted to UTF-8 bytes, otherwise it is preserved as a binary representation of the Arrayish data.
- object . sign ( transaction ) => Promise<hex>
- Returns a Promise that resolves to the signed transaction that is ready to be sent to the network.
- object . sendTransaction ( transaction ) => Promise<TransactionResponse>
- Sends the transaction (see Transaction Requests) to the network and returns a Promise that resolves to a Transaction Response. Any properties that are not provided will be populated from the network.